The Project “Method for monitoring bubble flow in an electrolyzer from shadow image and optical flow measurements” was approved for the last stage of Technology Readiness Levels (TRL) and is now patent eligible. The project proposes an approach for real-time monitoring of bubble flow from a membrane-free electrolyzer based on the optical flow approach using shadow images (Figure 1).
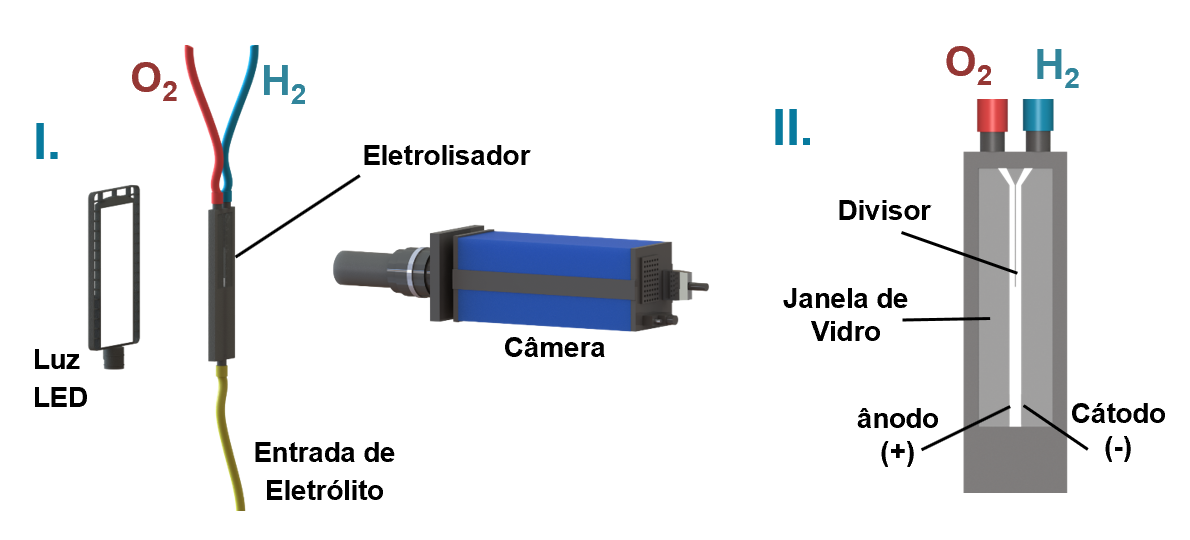
“Membraneless electrolyzers have economic advantages for the production of H2 from water electrolysis. Eliminating membranes or diaphragms from cell architecture reduces manufacturing costs and increases durability. In this equipment, H2 and O2 are generated simultaneously in each electrode due to an external electrical current. An electrolyte flow drags the gases to the outlet of the channel. High purity of the gaseous product requires that there is no crossing of the H2 plume with O2 or vice versa in the entire reactor. Based on this, monitoring bubble flow is essential for the proper functioning and optimization of membraneless electrolyzers. Bubble monitoring based on image analysis is often used in industrial equipment. However, existing methods fail when the bubble concentration is high”, says Rodrigo de Lima Amaral, Sc.D. and collaborating researcher at RCGI.
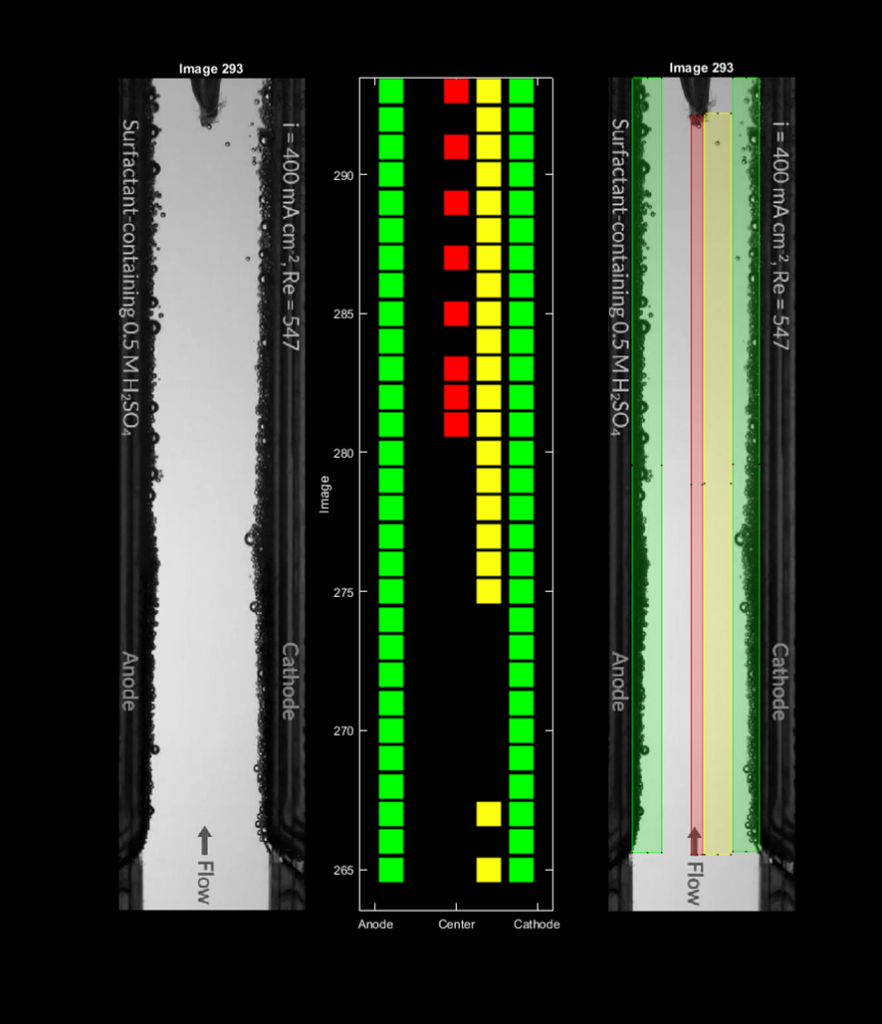
“When using optical flow it is possible to quantify the speed of one or a set of agglomerated bubbles without needing their individual identification, combined with the Farneback method to determine the pixel displacement of the image. Added to this, the interface that represents the temporal history of the presence of bubbles in different regions is used to facilitate decision-making during inspection (Figure 2)”, says Bernardo Luiz Harry Diniz Lemos, Sc.D. student in mechanical engineering at Poli-USP and researcher at the RCGI.
A demonstration of how the technology works can be seen in a video available on YouTube:
“The target market for this technology includes industries and professionals who can benefit from advanced monitoring of multiphase flows from the optimization of electrolysis processes, such as chemical and electrochemical processing industries and professionals, energy and sustainability companies, suppliers of industrial equipment and technologies”, adds Vítor Augusto Andreghetto Bortolin, Sc.D. in mechanical engineering at Poli-USP and researcher at RCGI.
The project is coordinated by Prof. Julio Meneghini, scientific director of RCGI.
Authors:
Bernardo Luiz Harry Diniz Lemos
Vítor Augusto Andreghetto Bortolin
Rodrigo de Lima Amaral
Caetano Rodrigues Miranda
Julio Romano Meneghini
Thiago Lopes
More information (pt-br): here.
More information (eng): here.